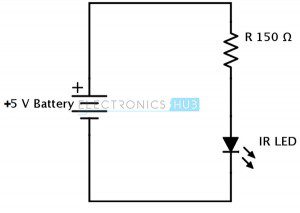
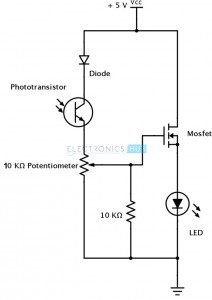
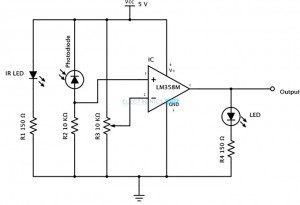
This Digital Door Lock – is simply a password based electronic code lock designed using 8051 micro controller, a keypad and a 12 volt dc relay. In this article, we have designed a simple digital door lock using 8051 -which can be used as a security checking system to limit access to an area/room only for certain individuals with the password. So our digital door lock project can be called with a very wide range of names like a digital combination lock using 8051 or a digital security code lock using 8051 microcontroller or a password security system using 8051 or an electronic code lock or a digital code lock using 8051. People call this kind of a “security system” with different names, though all of them mean to build a basic password based security system using a micro controller like 8051 or avr or pic or arduino (a controller of choice) with extra features like automatic door lock/opening facility, sound alarm, gsm based sms alert etc.
Digital Door Lock – Project Summary
Our Digital Code Lock project – is a simple electronic number lock system or an electronic combination lock using 8051 – which has a preset 5 digit password stored inside the program.The system collects 5 digit user input, compares the user input with the preset password inside program and if the user input and stored password matches, access will be granted (by opening the door with the help of relay for a few seconds and closing it automatically after stipulated time) . If there is a mismatch between user input and stored password, access will be denied (by not opening the closed door – that is by keeping the relay in OFF position)
Note:- We have a wonderful collection of
8051 projects which we have designed and published previously. Take a look If you are interested in building 8051 based applications and systems yourself! It’s a lot fun to learn and build new stuffs.
Lets get to building our password based digital door lock now.The circuit diagram of digital code lock is given below. Assemble the circuit as shown in diagram.
Password based Digital Door Lock/Electronic Code Lock – Circuit Diagram
Components Used
| 8051 – AT89S51 – 1 | 16×2 LCD Module – 1 |
|---|
| 4X4 Keypad – 1 | 10K Resistor Network – 1 |
| 12V Relay – 1 | |
| Transistor – BC548 – 1 | Diode – 1N4007 – 1 |
| Push Button Switch – 1 | Crystal – 11.059Mhz – 1 |
| Capacitors |
| 33pF -2 | 0.1uF -1 |
| 10uF -1 | 1 |
| Resistors |
| 10K Ohm – 1 | 100 Ohm -1 |
| 8.2K Ohm – 1 | 330 Ohm -1 |
| 4.7K Ohm – 1 | |
Connections Explained
Make the connections of digital code lock project as shown in circuit diagram. We have explained the connections below.
Keypad to 8051 – In this particular electronic code lock project, we have interfaced a 4×4 keypad to Port 3 of 8051 micro controller. Row pins are connected from P3.0 to P3.3, whereas Column pins are connected from P3.4 to P3.7. Read our tutorial on
interfacing keypad to 8051 – to learn how keypad is connected to 8051 and how key presses are identified and displayed.
16×2 LCD Module to 8051 – We are using a 16×2 lcd module to display status messages of the project. We have connected this LCD module in 8 bit mode (using 8 data lines). The 8 data lines are connected to Port 0 of 8051.An external pull up resistance is connected using a 10K Resistor Network (with 8 pins) at Port 0 to interface the 8 data lines of LCD. The LCD controlling pins RS, R/W and E are connected to Port 2 pins P2.7, P2.6 and P2.5 respectively. Read our tutorial on
interfacing LCD to 8051 – to learn how to connect LCD module to 8051 properly and also to learn how to display text messages on the LCD module perfectly.
Push button switch – is used to setup reset circuit of 8051 and Crystal is used to provide necessary clock to 8051.
Relay – a 12V SPDT relay is used for the digital door lock project and is connected to P2.0. A transistor (BC548) – is used to drive the relay with necessary current.
Working of the Project
Objective of the Digital Door Lock project is to allow access to people who input the 5 digit password correctly and to not allow access to people who input password wrongly. We use a 4×4 Keypad to input digits to micro controller and a 12V relay is used to control the electronic solenoid lock (not shown in circuit diagram) of door. The password is stored inside the 8051 program (program memory). In the example program given below, we use password 12345 and is stored in program memory location with label – PASSW.
PASSW: DB 49D,50D,51D,52D,53D,0 // Decimal equivalent of 1,2,3,4,5 is stored in address label PASSW
When we turn power supplies ON, the system will turn ON with a messaged on LCD screen – “Password Based Security System”. Once the boot up process is complete, the system will ask to “Input 5 Digits”. The user has to input 5 digits consecutively after this message appears on LCD screen. Once 5 digits are entered, the system will start checking password (by comparing the input 5 digits with the stored password). Before the subroutine to check password (comparison subroutine – with label – CHECK_PASSWORD) begins, a status message “Checking Password” will be displayed on LCD module. The password checking subroutine will compare each entered digit – one by one and if all the 5 digits are entered correctly (i.e each entered digit matches with the stored password in order) the system will begin the process of allowing access to the user by turning ON the relay( achieved with SETB P2.0 command in program). Two messages will be displayed on LCD screen – “Access Granted” and “Door Opens” . The relay will be turned OFF with command CLR P2.0 after a few seconds (that is in the next iteration of the MAIN Program commands) If the password entered is wrong, the system will not turn ON the relay and a message “Wrong Password” – “Access Denied” will be displayed on LCD screen.
Program/ Code – Password Based Security System
RS EQU P2.7
RW EQU P2.6
E EQU P2.5
SEL EQU 41H
ORG 000H
CLR P2.0
MOV TMOD,#00100001B
MOV TH1,#253D
MOV SCON,#50H
SETB TR1
ACALL LCD_INIT
MOV DPTR,#TEXT1
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL LINE2
MOV DPTR,#TEXT2
ACALL LCD_OUT
MAIN:ACALL LCD_INIT
MOV DPTR,#TEXT1
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL LINE2
MOV DPTR,#TEXT2
CLR P2.0
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL DELAY1
ACALL DELAY1
ACALL READ_KEYPRESS
ACALL LINE1
MOV DPTR,#CHKMSG
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL DELAY1
ACALL CHECK_PASSWORD
SJMP MAIN
LCD_INIT: MOV DPTR,#INIT_COMMANDS
SETB SEL
ACALL LCD_OUT
CLR SEL
RET
LCD_OUT: CLR A
MOVC A,@A+DPTR
JZ EXIT
INC DPTR
JB SEL,CMD
ACALL DATA_WRITE
SJMP LCD_OUT
CMD: ACALL CMD_WRITE
SJMP LCD_OUT
EXIT: RET
LINE2:MOV A,#0C0H
ACALL CMD_WRITE
RET
LINE1: MOV A,#80H
ACALL CMD_WRITE
RET
CLRSCR: MOV A,#01H
ACALL CMD_WRITE
RET
CMD_WRITE: MOV P0,A
CLR RS
CLR RW
SETB E
CLR E
ACALL DELAY
RET
DATA_WRITE:MOV P0,A
SETB RS
CLR RW
SETB E
CLR E
ACALL DELAY
RET
DELAY: CLR E
CLR RS
SETB RW
MOV P0,#0FFh
SETB E
MOV A,P0
JB ACC.7,DELAY
CLR E
CLR RW
RET
DELAY1:MOV R3,#46D
BACK: MOV TH0,#00000000B
MOV TL0,#00000000B
SETB TR0
HERE1: JNB TF0,HERE1
CLR TR0
CLR TF0
DJNZ R3,BACK
RET
DELAY2: MOV R3,#250D
BACK2: MOV TH0,#0FCH
MOV TL0,#018H
SETB TR0
HERE2: JNB TF0,HERE2
CLR TR0
CLR TF0
DJNZ R3,BACK2
RET
READ_KEYPRESS: ACALL CLRSCR
ACALL LINE1
MOV DPTR,#IPMSG
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL LINE2
MOV R0,#5D
MOV R1,#160D
ROTATE:ACALL KEY_SCAN
MOV @R1,A
ACALL DATA_WRITE
ACALL DELAY2
INC R1
DJNZ R0,ROTATE
RET
CHECK_PASSWORD:MOV R0,#5D
MOV R1,#160D
MOV DPTR,#PASSW
RPT:CLR A
MOVC A,@A+DPTR
XRL A,@R1
JNZ FAIL
INC R1
INC DPTR
DJNZ R0,RPT
ACALL CLRSCR
ACALL LINE1
MOV DPTR,#TEXT_S1
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL LINE2
ACALL DELAY1
SETB P2.0
MOV DPTR,#TEXT_S2
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL DELAY1
SJMP GOBACK
FAIL:ACALL CLRSCR
ACALL LINE1
MOV DPTR,#TEXT_F1
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL DELAY1
ACALL LINE2
MOV DPTR,#TEXT_F2
ACALL LCD_OUT
ACALL DELAY1
GOBACK:RET
KEY_SCAN:MOV P3,#11111111B
CLR P3.0
JB P3.4, NEXT1
MOV A,#49D
RET
NEXT1:JB P3.5,NEXT2
MOV A,#50D
RET
NEXT2: JB P3.6,NEXT3
MOV A,#51D
RET
NEXT3: JB P3.7,NEXT4
MOV A,#65D
RET
NEXT4:SETB P3.0
CLR P3.1
JB P3.4, NEXT5
MOV A,#52D
RET
NEXT5:JB P3.5,NEXT6
MOV A,#53D
RET
NEXT6: JB P3.6,NEXT7
MOV A,#54D
RET
NEXT7: JB P3.7,NEXT8
MOV A,#66D
RET
NEXT8:SETB P3.1
CLR P3.2
JB P3.4, NEXT9
MOV A,#55D
RET
NEXT9:JB P3.5,NEXT10
MOV A,#56D
RET
NEXT10: JB P3.6,NEXT11
MOV A,#57D
RET
NEXT11: JB P3.7,NEXT12
MOV A,#67D
RET
NEXT12:SETB P3.2
CLR P3.3
JB P3.4, NEXT13
MOV A,#42D
RET
NEXT13:JB P3.5,NEXT14
MOV A,#48D
RET
NEXT14: JB P3.6,NEXT15
MOV A,#35D
RET
NEXT15: JB P3.7,NEXT16
MOV A,#68D
RET
NEXT16:LJMP KEY_SCAN
INIT_COMMANDS: DB 0CH,01H,06H,80H,3CH,0
TEXT1: DB "PASSWORD BASED",0
TEXT2: DB "SECURITY SYSTEM",0
IPMSG: DB "INPUT 5 DIGITS",0
CHKMSG: DB "CHECKING PASSWORD",0
TEXT_S1: DB "ACCESS - GRANTED",0
TEXT_S2: DB "DOOR OPENED",0
TEXT_F1: DB "WRONG PASSWORD",0
TEXT_F2: DB "ACCESS DENIED",0
PASSW: DB 49D,50D,51D,52D,53D,0
END
The program is written in assembly language. The important aspects and subroutines of the program are explained below.
KEY_SCAN – is the subroutine to identify a key press. The method of column scanning is employed in identifying the pressed key. The pressed key is identified and is assigned a decimal equivalent value (ASCII value) of the pressed key. You may read the
tutorial on keypad to 8051 – interfacing to learn more about the programming.
READ_KEYPRESS – is the subroutine to collect user inputs. A counter is set up using register R0 to count 5 times (this will limit the user input collection to first 5 key presses). Register R1 is assigned address location 160D. The collected user inputs are saved in address location starting from 160D. This location is incremented successively using INC R1 – command of 8051. So first user input is stored in 160D, second user input in 161D, third in 162D, fourth in 163D and fifth user input in 164D. These address locations are accessed using register R1 via
indirect addressing method.
Note:- There are two delay routines written in the program. DELAY1 – is used as a delay for outputting messages on LCD module properly. After sending a message/data to LCD module, DELAY1 is called so that the message stays on LCD screen for the stipulated delay time. DELAY2 (is a 2.5 seconds delay) is used to provide the necessary debouncing effect for the keypad. (A push button switch or any kind of mechanical switch has
bouncing effect. This effect has to be nullified either with a capacitor or with some tweaks inside software – for example – a 1 or 2 seconds delay after a key press is scanned)
CHECK_PASSWORD – is the subroutine to compare user input password (5 digits) with the actual stored password in the program. Comparison is made digit by digit by selecting each digit from stored password with the help of DPTR and loading it to Accumulator (with MOVC A,@A+DPTR). Each digit loaded to accumulator is then compared with the corresponding digit stored as user input (in address locations 16D to 164D) by loading them one by one to register R1. Digits are compared by X-OR ing them with command XRL A,@R1. Based on the outcome of comparison, this subroutine has commands written to either allow access (and turn ON relay) or to not allow access and display an “Access Denied” message on LCD screen.
Conclusion
So that’s all about the Password based Security System using 8051. We hope you have understood the circuit, its working and the program really well. If you have any doubts,please ask in comments section. If you would like to learn more interesting and similar projects like this electronic password lock, take a look at the following security system/lock projects.
RFID based Security System using 8051 – is a security system very similar to Digital Door Lock or Electronic Code Lock in concept. The major difference in this project is that, unique RFID Tags are used to identify authorized personnel (instead of keypad and password). An RFID reader is interfaced to 8051 to read RFID Tags.
Digital Code Lock -Advanced -using Arduino – is a very interesting and advanced version of Digital Code Lock projects built using keypad and arduino. The most interesting part of this project is “User Defined Password” option where the user can set a password himself at the time of installation of system. This SET password at installation can be later changed/